In the world of electrical installations, choosing the right lead cable is crucial. Expert Mark Johnson, a senior technician with over 15 years of experience, emphasizes, "The right lead cable can make all the difference in system performance." Lead cables come in various types, each tailored for specific applications. From flexible cables used in machinery to heavy-duty options designed for industrial environments, understanding these differences is essential.
Every lead cable type has its unique strengths and weaknesses. For instance, some cables offer excellent conductivity, while others provide superior resistance to environmental factors. This diversity can create confusion for consumers, often leading to poor choices. Reflecting on mistakes made in past projects can help inform better decisions in the future. Employing the right lead cable speeds up installations and enhances safety and efficiency.
Navigating through the myriad of options might seem overwhelming. It's important to recognize that not all cables are created equal. A mismatched lead cable can compromise an entire system. Thus, a careful selection process is more than just a technical requirement; it's a step towards a more effective electrical solution.
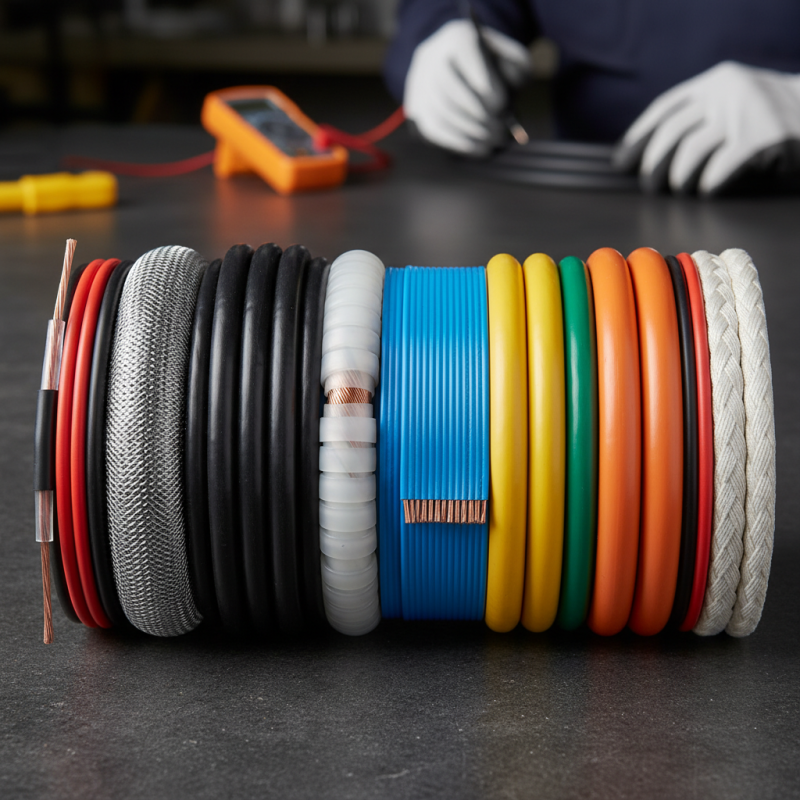

Lead cables are essential in electrical applications. They provide a reliable connection between power sources and devices. Understanding their basics can help you make informed choices.
Lead cables come in various types, each with unique features. Some are designed for high flexibility, while others are built for durability. Consider factors like insulation, conductivity, and temperature rating. It's critical to match the cable type with your specific requirements.
Not all lead cables are created equal. Quality can vary significantly. Always verify the specifications before purchasing. Also, evaluate your installation conditions. Sometimes, the cable may not perform as expected due to environmental factors. Always plan ahead and consider future needs.
| Cable Type | Application | Voltage Rating | Current Rating | Insulation Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XLPE Cable | Residential Wiring | 600V | 20A | Cross-linked Polyethylene |
| PVC Cable | General Wiring | 300V | 15A | Polyvinyl Chloride |
| Rubber Cable | Outdoor Use | 500V | 30A | Rubber |
| Armored Cable | Commercial Installations | 600V | 25A | Steel Armor |
| Silicone Rubber Cable | High-Temperature Applications | 1000V | 20A | Silicone Rubber |
| Submersible Pump Cable | Water Pumps | 600V | 15A | PVC with Water-Resistant Coating |
| Twisted Pair Cable | Data Transmission | 300V | 12A | LDPE Insulation |
| High Voltage Cable | Industrial Applications | 35kV | 500A | Cross-linked Polyethylene |
| Communication Cable | Telecommunications | 250V | 10A | Polyethylene |
When choosing lead cable materials, understanding their unique characteristics is vital. Different types serve diverse electrical needs. For instance, copper leads are renowned for their excellent conductivity. They are often lightweight and flexible, making installation easier. However, their cost can be higher than other materials. Additionally, they may not perform well in corrosive environments.
Aluminum cables offer a balance of weight and cost. They are lighter than copper, but with lower conductivity. This can lead to energy losses in long runs. Yet, they are often used in overhead lines because they resist corrosion well. Another option, rubber-insulated lead cables, provide great flexibility under harsh conditions. They resist abrasion and are often used in portable machinery. This variety is essential to ensure safety and efficiency in electrical systems.
When selecting lead cables, several critical factors influence the decision. Voltage rating stands out. Depending on the application, the correct voltage rating prevents insulation failure. A study by the International Electrotechnical Commission notes that improper voltage ratings account for 30% of electrical failures in residential projects. Understanding the specific voltage requirements for your setup is paramount.
Another key element is the cable's material. Different materials offer varying conductivity levels and durability. Copper is widely regarded for its excellent conductivity. However, it’s generally more expensive. On the other hand, aluminum is lightweight and cheaper but less efficient. Industry data shows that aluminum cables can lose up to 15% of electrical energy compared to copper configurations. This energy loss can lead to higher long-term costs, affecting both budgeting and environmental impact.
Cable insulation types are equally crucial. The insulation materials must match the application environment. Thinner insulation may not withstand moisture or heat, leading to premature failure. Research from the National Electrical Manufacturers Association indicates that nearly 40% of installation issues stem from inadequate insulation. This highlights the necessity of meticulous planning and understanding of environmental factors before making a choice.
When it comes to lead cables, the choice of material is crucial. PVC, rubber, and silicone cables each offer unique benefits for different applications. PVC cables are cost-effective and widely used. They provide decent insulation and are suitable for indoor use. However, their flexibility can be limited in colder temperatures. This can be a significant drawback.
Rubber cables stand out for their durability and flexibility. They perform well in extreme temperatures. This makes them ideal for outdoor applications. But they often come with a higher price tag. Users should consider their environment before making a choice. While rubber offers great performance, it may not be necessary for less demanding applications.
Silicone cables are another option. They maintain flexibility and performance in a range of temperatures. Their high resistance to environmental factors is appealing. However, silicone cables can be pricier than their PVC counterparts. It’s worthwhile to analyze the specific needs of your project. Understand how each type will perform in real-world scenarios.
Tips: Always assess environmental conditions before selecting a lead cable. This can save time and money in the long run. Regularly inspect cables for any signs of wear and tear. It’s better to change a cable early than to face failures later.
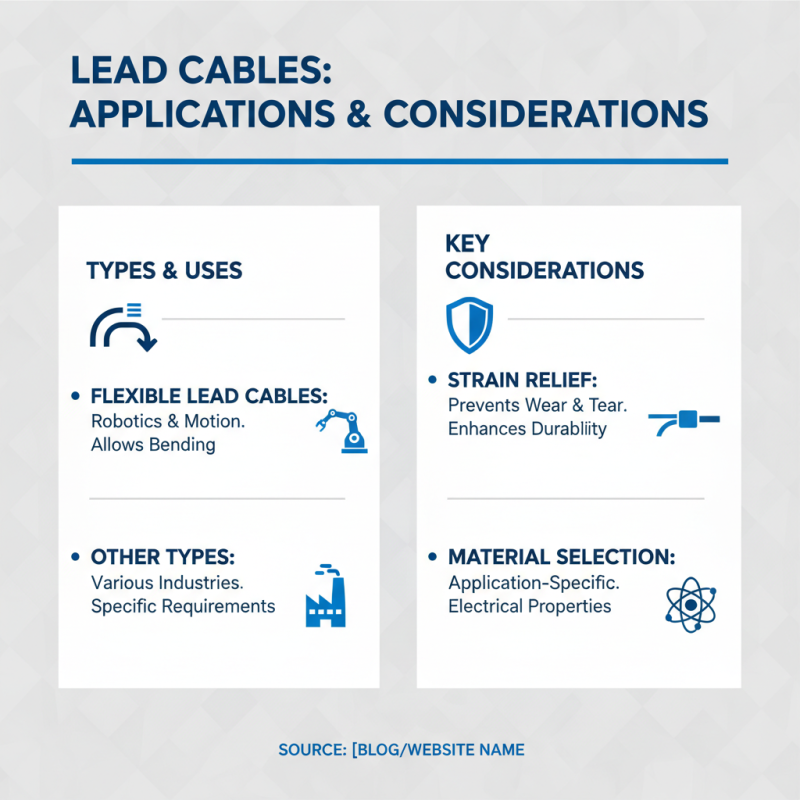
When selecting lead cables for electrical applications, understanding their specific uses is crucial. Many industries utilize different types of lead cables based on their requirements. For instance, flexible lead cables are popular in robotics. They allow easy movement and bending without breaking. It's important, though, to consider strain relief measures to prevent wear over time.
Another type is the high-voltage lead cable. This cable type is essential in power generation and transmission. Users must ensure proper insulation to prevent short circuits. Otherwise, catastrophic failures can occur. On the other hand, low-voltage lead cables are typical in residential settings. They are ideal for lighting and small appliances. Yet, one must not overlook the importance of correct wire sizing to avoid overheating.
Lead cables may also find use in automotive applications. They connect various components, like batteries to starters. Choosing the right gauge is vital here, too. Undersizing can lead to voltage drops or even fire hazards. Clearly, while lead cables serve many functions, attention to detail and proper application are critical.


At Radix, we do more than sell products; we provide solutions. We take the time to learn about each customer and your unique challenges, and then our knowledgeable team of problem solvers works to educate you on the possibilities to improve your products or operations.
From cutting-edge technology applications to extreme industrial environments, we’re here to collaborate, innovate, and elevate your success. Let’s connect.
