Choosing the right high temperature cable for specific applications is critical. Industries like aerospace and automotive have stringent requirements for materials. Research shows that high temperature cables must endure extreme conditions and maintain performance. According to industry reports, the global high temperature cable market is projected to grow by 4.5% annually until 2025. This growth reflects increased demand in various sectors, emphasizing the importance of selecting suitable materials.
In applications where heat resistance is essential, high temperature cables must not only withstand high temperatures but also resist degradation. These cables often use materials like silicone or fluoropolymer. The wrong choice can lead to failures, safety issues, and additional costs. A report by a leading industry analyst indicates 30% of equipment failures stem from inadequate cabling solutions. Selecting the right high temperature cable is not just a technical decision; it impacts reliability and efficiency.
Many professionals overlook installation factors when choosing cables. Environmental conditions and installation methods play a vital role. A seemingly small oversight can lead to significant performance issues. It’s essential to consider these factors closely when assessing high temperature cable options, ensuring optimal results in demanding applications.

High temperature cables are essential in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. These cables are designed to operate effectively in extreme heat environments. For example, reports indicate that temperatures can exceed 200 degrees Celsius in some applications. Therefore, choosing the right high temperature cable is crucial.
Understanding the materials used in high temperature cables is vital. Common materials include silicone, fluoropolymers, and high-temperature nylon. Each material offers different benefits. Silicone is flexible and has good thermal stability. Fluoropolymers provide chemical resistance and durability. These features make them suitable for different applications. Yet, these materials can also pose challenges. They may not excel in all environments, requiring careful evaluation.
Considering specific requirements is important when selecting cables. Factors like thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and flexibility must align with your application. A comprehensive analysis shows that 25% of applications suffer from improper cable choice. This statistic highlights the need for thorough research. Relying on expert recommendations can help prevent costly mistakes. Choosing high temperature cables demands diligence and an understanding of your operational conditions.
When selecting high temperature cables, understanding application needs is crucial. Different industries have varied thermal requirements. For instance, aerospace applications might demand cables that can withstand temperatures exceeding 200°C, while industrial settings may only need cables rated for 150°C. Material choice plays a pivotal role. For example, silicone rubber and fluoropolymers are popular due to their high thermal resistance and flexibility.
Additionally, insulation thickness can impact performance. Thicker insulation improves heat resistance but may add bulk. It's a trade-off that merits consideration. Furthermore, evaluating the environment where the cables will operate is essential. Exposure to chemicals or physical stressors can degrade cable materials over time.
A study by the International Electrotechnical Commission highlights that improper cable selection can lead to failures in up to 40% of applications, underscoring the need for careful consideration.
Overall, be wary of overspecifying or undervaluing application demands. The lasting integrity of a high temperature cable depends on a combination of factors. Some may overlook temperature ratings in favor of cost or availability. This can lead to increased maintenance and replacement costs. Balancing all these elements is vital for ensuring reliability and longevity in your applications.
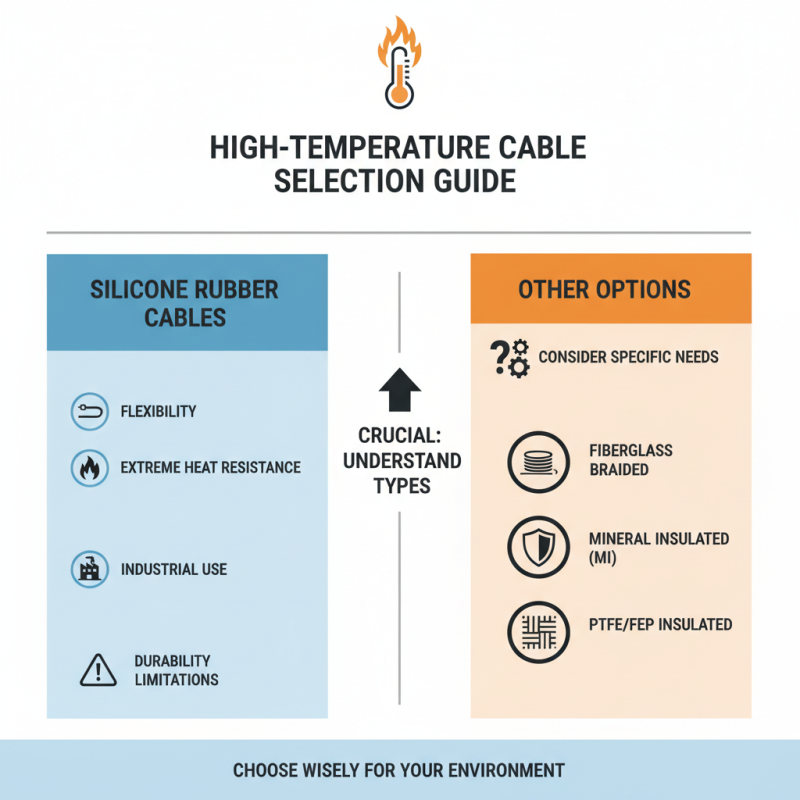
When selecting high-temperature cables, understanding the types available is crucial. There are several options to consider based on your specific needs. Silicone rubber cables offer flexibility and resistance to extreme conditions. They are commonly used in industrial applications. However, their durability may not always meet the demands of certain environments.
Another type is PTFE (Teflon) cables. These can withstand higher temperatures and resist chemical exposure well. They perform excellently in aerospace and military applications. Still, their cost may be a concern for some projects. In harsh conditions, glass fiber cables shine with their robustness and lightweight features. However, they may require careful handling to avoid damage.
Lastly, inorganic cables are available. These are suitable for high temperatures over long periods. They provide excellent insulation. Note that installation can be tricky. It’s essential to choose the right type based on the application. Evaluating your environment and requirements will lead to a more effective decision.
Choosing the right high-temperature cable is essential for your applications. Performance specifications are crucial in ensuring that the cable can withstand extreme conditions. First, consider the temperature rating. Cables are often rated for specific temperature ranges. A cable with a higher temperature rating will have better durability.
Next, examine the insulation material. Different materials offer varied levels of heat resistance. Common options include silicone, PTFE, and PVC. Each material has its strengths and weaknesses. Silicone, for instance, can handle high temperatures well. However, it may not be as durable in harsh mechanical environments.
Another important specification is flexibility. High-temperature cables should maintain flexibility, even in extreme conditions. A stiff cable can lead to installation challenges. Additionally, check for abrasion resistance. Cables in rugged environments need to endure wear and tear. Sometimes, a cable that seems adequate in theory performs poorly in practice. Testing under actual conditions is always recommended.
| Specification | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | The maximum temperature the cable can withstand during operation. | -40°C to 260°C |
| Voltage Rating | The maximum voltage the cable can handle safely. | 600V to 1000V |
| Conductor Material | Material used for the conductor, affecting conductivity and heat resistance. | Copper or Aluminum |
| Insulation Material | Material that encases the conductor, providing electrical insulation. | PTFE, FEP, Silicone |
| Shielding | Protection against external EMI/RFI interference. | Foil or Braid Shielding Options |
| Fire Resistance | Ability to withstand fire and prevent flames from spreading. | UL 94 V-0 or better |
| Flexibility | The cable's ability to bend and flex without damage. | Highly Flexible or Standard Flex Types |
High-temperature cables are essential in various applications, particularly in industrial settings. Installation should be done carefully. Improper handling can lead to premature failure. According to a recent industry report, over 30% of cable failures are due to installation errors. Ensure that cables are not subjected to unnecessary bending or twisting. This reduces internal damage. Proper support hardware is crucial.
Maintenance is equally important for high-temperature cables. Regular inspections can help identify wear and tear. Experts recommend a visual check every six months. Electrical testing should be performed annually to assess performance. Monitor for signs of heat stress, such as discoloration or insulation damage. A study by the Electrical Safety Foundation revealed that 25% of electrical fires are linked to faulty cables. Keeping cables clean and free from contaminants is vital for longevity.
User training also plays a key role. Ensure that personnel understand handling procedures. They should know what can damage the cables. Misunderstandings in this area can lead to costly repairs. Remember, high-temperature cables must be paired with suitable connectors and accessories. This is often overlooked, yet it can greatly affect performance.





At Radix, we do more than sell products; we provide solutions. We take the time to learn about each customer and your unique challenges, and then our knowledgeable team of problem solvers works to educate you on the possibilities to improve your products or operations.
From cutting-edge technology applications to extreme industrial environments, we’re here to collaborate, innovate, and elevate your success. Let’s connect.
