Choosing the right lead wire for your electrical projects is a crucial decision that can greatly impact performance and safety. As Larry Thompson, a seasoned electrical engineer with over 20 years of experience in the industry, aptly states, “Selecting the proper lead wire not only enhances efficiency but also ensures the longevity of your installations.” With countless options available, from various materials to gauge sizes, the process can be daunting for both novice and experienced professionals alike.
In today's fast-paced technological landscape, the significance of lead wire cannot be overstated. It serves as the vital link in electrical connections, affecting everything from signal integrity to power delivery. The right lead wire must be chosen to match the specific requirements of the project, including the type of application, environmental conditions, and load capacities. As you navigate this selection process, it's essential to consider not only the technical specifications but also factors such as insulation type, flexibility, and temperature ratings.
Ultimately, making an informed choice in lead wire selection is not just about meeting immediate project needs; it lays the foundation for the reliability and safety of your electrical systems. By understanding the various characteristics and applications of lead wire, you can ensure optimal performance and reduce the risk of potential failures.
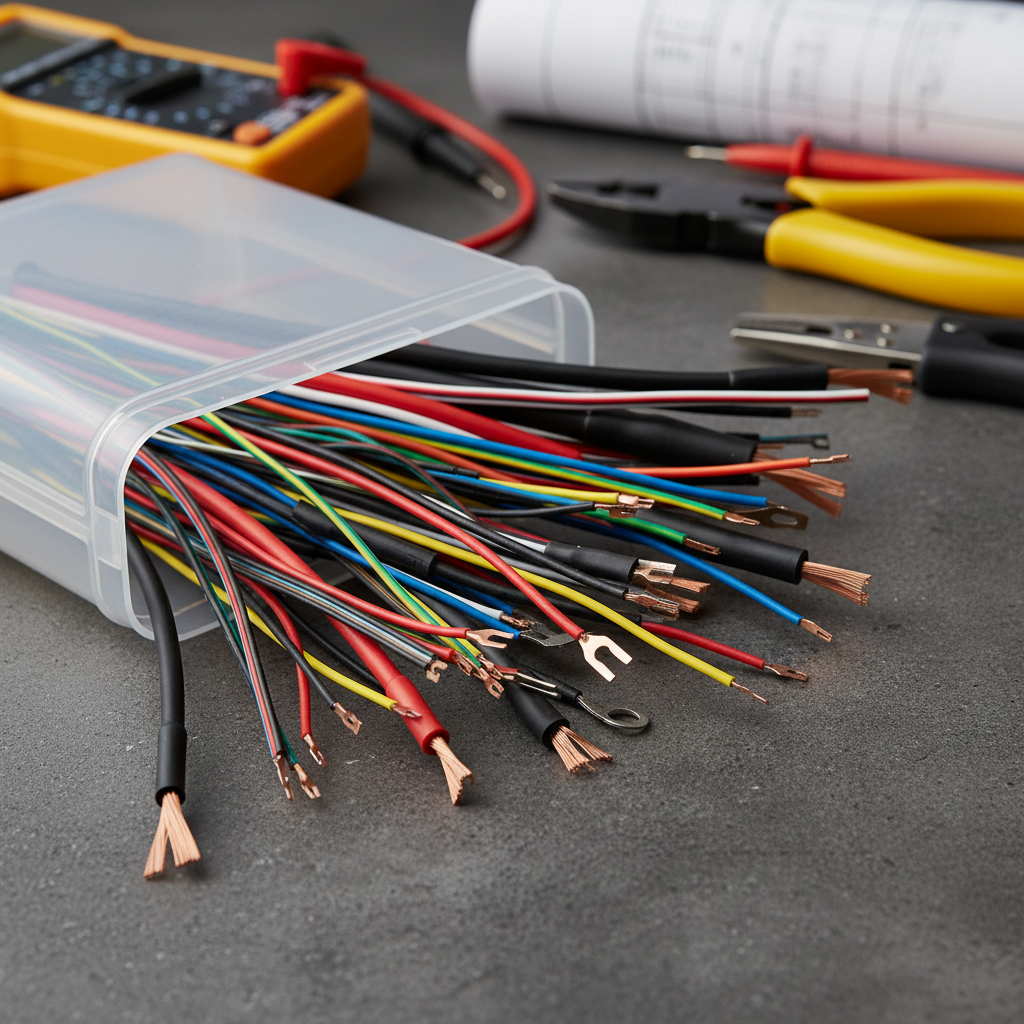
Lead wires are crucial components in electrical projects, serving as the conduits for transmitting electricity between different parts of a circuit. Understanding their significance can enhance the reliability and efficiency of your electrical systems. Choosing the right lead wire ensures optimal performance, minimizes energy loss, and prevents potential hazards such as overheating and short circuits.
When selecting lead wires, consider factors such as conductor material and insulation type. Copper wires are popular due to their excellent conductivity, while aluminum offers a lightweight alternative. Additionally, the insulation material—such as PVC, silicone, or Teflon—should be chosen based on the operating environment. For example, silicone insulation is ideal for high-temperature applications, while PVC is sufficient for general use.
**Tips:** Always verify the voltage and current ratings of the lead wire to match the requirements of your project. Furthermore, evaluating the wire gauge is essential; a thicker wire can carry more current, reducing the risk of overheating. Lastly, consider the flexibility of the lead wire for applications that require bending or twisting, ensuring easy maneuverability without compromising performance.
When selecting lead wires for your electrical projects, understanding the different types of materials available is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and safety. Lead wires are commonly made from copper, aluminum, or various alloys.
Copper is the most widely used material due to its excellent conductivity, which is nearly 60% more efficient than aluminum. According to the International Journal of Electrical Engineering, copper wires typically exhibit a resistance as low as 0.017 ohm-mm²/m, making them an ideal choice for applications requiring high current capacity.
On the other hand, aluminum lead wires are often preferred for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. Although aluminum has a greater resistance—approximately 1.68 times that of copper—it is about one-third the weight, providing significant advantages in specific contexts. A report from the International Electrotechnical Commission highlighted that the use of aluminum in cabling can reduce overall structural weight by up to 30%, thereby improving fuel efficiency in vehicles.
When deciding on a lead wire type, consider the working environment as well. For instance, PVC-insulated lead wires are suitable for general applications, while silicone insulation is better for high-temperature settings, withstanding temperatures up to 200°C. Selecting the right lead wire material tailored to your project's specific requirements can significantly impact both performance and longevity.
When selecting the right lead wire for your electrical projects, determining the required gauge is essential. The gauge of the wire affects its current-carrying capacity, flexibility, and resistance, all of which play a vital role in the performance and safety of your project. Generally, a lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire that can handle more current, while a higher number signifies a thinner wire. It's crucial to consider the specific demands of your application, such as voltage and load requirements, when making your choice.
Tips: To ensure you select the appropriate gauge, always refer to wire gauge charts that illustrate the ampacity of different gauges. Additionally, consider factors such as the length of the wire run and the environment in which the wire will be used. For instance, longer runs may require thicker wire to compensate for voltage drops, while wires exposed to harsh conditions might need insulation rated for those environments.
In planning your project, assess both the electrical requirements and any physical limitations. For example, if space is tight, you may need to balance between wire thickness and flexibility. Consult extensive recommendations from manufacturers to guide your decision-making process. By being methodical in your gauge selection, you can enhance the reliability and efficiency of your electrical projects.

When selecting lead wires for electrical projects, evaluating temperature ratings is crucial to ensuring both safety and performance. Each electrical application operates under specific temperature conditions, and the lead wire must be able to withstand these temperatures without compromising its integrity. Using wires that exceed their rated temperature can lead to insulation breakdown, increased resistance, and ultimately, failure of the electrical system. Therefore, understanding the temperature environment in which the wire will operate is essential for making an informed choice.
Moreover, different materials offer varying temperature resistance. For example, silicone-insulated lead wires are more suitable for high-temperature applications compared to PVC-insulated wires. Choosing the right material that aligns with the intended operating conditions is paramount. By carefully assessing these factors, you can enhance the reliability and longevity of your electrical projects while minimizing risks associated with thermal stress. This proactive approach not only ensures safety but also improves overall performance in the long run.
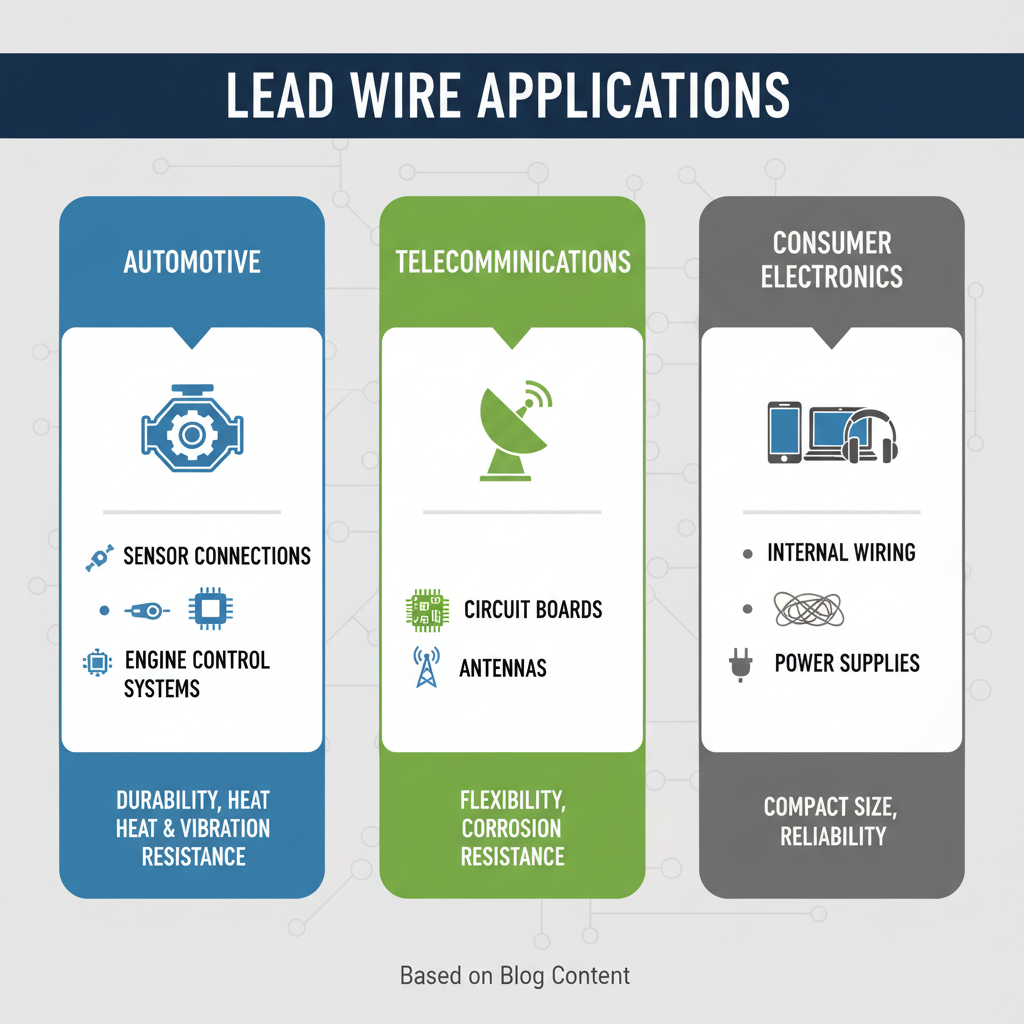
When selecting lead wire for electrical projects, it's essential to consider its common applications to ensure optimal performance. Lead wires are widely used in various fields, including automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. For instance, in automotive applications, a reliable lead wire is critical for sensor connections and engine control systems where durability and resistance to heat and vibrations are paramount. In telecommunications, lead wires connect various components such as circuit boards and antennas, requiring flexibility and corrosion resistance to maintain signal integrity.
Best practices for lead wire usage involve choosing the correct gauge and material based on the specific requirements of the project. Thicker wires can handle higher currents but may be less flexible, while thinner wires offer more maneuverability at the cost of current capacity. Additionally, insulation material should be selected based on environmental factors; for instance, PVC is commonly used for indoor applications, while silicone or PTFE is better suited for high-temperature environments. Proper termination techniques, such as soldering or using connectors, also play a crucial role in ensuring a reliable and safe connection within your electrical projects.






At Radix, we do more than sell products; we provide solutions. We take the time to learn about each customer and your unique challenges, and then our knowledgeable team of problem solvers works to educate you on the possibilities to improve your products or operations.
From cutting-edge technology applications to extreme industrial environments, we’re here to collaborate, innovate, and elevate your success. Let’s connect.
