In the world of electrical projects, understanding different wire cable types is crucial. Wire cables are the lifeblood of any electrical system. According to industry reports, the global wire and cable market was valued at over $200 billion in 2021, showcasing its importance. As projects become more complex, the demand for diverse wire cable types grows.
From residential wiring to industrial applications, each wire cable serves a unique purpose. For instance, THHN wire is popular for its durability and versatility. Meanwhile, network cables, like Cat6, play a vital role in data transmission. However, many individuals overlook the specifications of wire cables, which can lead to project failures.
Choosing the right wire cable demands careful consideration. Missteps often occur due to a lack of knowledge or clarity. It's essential to reflect on the specific needs of your project to select the ideal wire cable. Understanding these elements will enhance the efficiency and safety of your installations.
Wire cables are fundamental in various projects. Understanding the different types of wire cables can save time and resources. An analysis by the International Wire and Cable Association indicates that the global wire and cable market is projected to reach $250 billion by 2026. This growth underscores the importance of selecting the right cable type.
Copper and aluminum cables are the most common. Copper offers excellent conductivity and durability. However, it is more expensive than aluminum. The difference in conductivity can lead to inefficiencies. In contrast, aluminum cables are lighter and less costly. They can be a good option for overhead power lines, as long as engineers account for their lower strength.
Another significant type includes fiber optic cables. They provide high-speed data transmission. However, they can be brittle and require specialized installation techniques. Data from market research shows that the demand for fiber optic cables is increasing, especially in urban areas. Yet, many projects overlook the need for proper installation and maintenance, which can lead to performance issues down the line.
When selecting wire cable types for projects, understanding their key characteristics is crucial. Copper and aluminum are common materials. Copper is known for its excellent conductivity, while aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective. According to industry reports, copper cables can handle higher currents, making them suitable for demanding applications. However, aluminum cables need larger diameters to match copper's conductive capacity.
Insulation type is another important aspect. PVC insulation is widely used due to its flexibility and resistance to moisture. On the other hand, rubber insulation offers better temperature resistance. As per recent data, 30% of electrical fires are caused by faulty wiring. This statistic highlights the importance of using the right insulation with proper ratings.
The cable configuration is equally significant. Stranded cables are flexible and easier to work with. Solid cables provide better conductivity but are less adaptable. It's essential to analyze the specific needs of each project. A mismatch can lead to inefficiencies or even safety hazards. Many projects have failed due to improper wire type selection. Understanding these characteristics will help avoid common issues.
When working on various projects, understanding wire cable types is crucial. Different applications require different cables. For instance, building construction often demands THHN wire for its heat-resistant properties. This type can endure temperatures up to 90°C, making it ideal for residential and commercial use. In the transportation sector, however, XLPE cables shine due to their high voltage resistance, which can withstand harsh conditions.
Marine projects frequently use marine-grade cables to resist corrosion. This type of cable has a special insulation coating that protects it against saltwater. According to industry reports, up to 25% of cable failures in marine environments result from corrosion. Therefore, selecting the right type of cable can significantly enhance the project’s longevity.
Data shows that improperly chosen cables can lead to inefficiencies. For example, using lower gauge wires may cause overheating and potential failures. This highlights the importance of understanding the specific needs of each project. Evaluating insulation type, voltage capacity, and installation environment is essential. Uninformed decisions can result in project delays or costly rewiring.
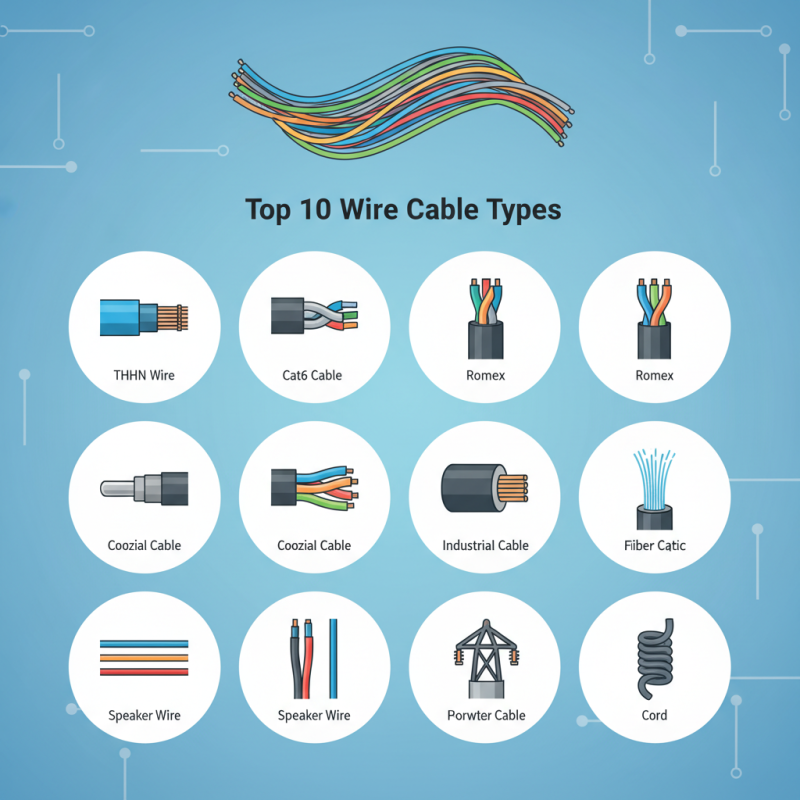
This chart displays the top 10 types of wire cables commonly used in various projects, illustrating their application frequencies. Each type serves a unique purpose and is essential in electrical and networking projects.

When selecting wire cable types for your projects, various factors must be considered. The wire's functionality is critical. Different applications require different cable specifications. For instance, a report from the International Electrotechnical Commission indicates that using the wrong cable type can lead to over 30% of electrical failures in systems. Choose cables that match the intended use.
Another consideration is the environment where the cable will be installed. Cables exposed to extreme temperatures or moisture require special insulation. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, choosing the wrong insulation can significantly diminish a cable's lifespan, leading to costly replacements.
Lastly, gauge selection plays a vital role. Thicker cables can manage greater currents but are less flexible. The American Wire Gauge system provides a standard for wire thickness, but many still underestimate its importance. A miscalculation can result in overheating or inefficient operation. Consider all factors carefully to avoid oversights that might cause malfunction or damage.
When working with wire cables, safety standards and regulations are essential. They ensure that projects meet necessary guidelines. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), specific requirements cover insulation, grounding, and ampacity. Failure to comply can lead to severe consequences, including electrical fires and safety hazards.
Understanding the risks is crucial. Many installations overlook proper cable ratings, exposing users to dangers. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that electrical accidents contribute to numerous injuries annually. Familiarizing yourself with codes like the NEC can prevent these incidents.
**Tip:** Always check local regulations. They may differ from national standards.
Another concern is environmental safety. Many cables contain harmful materials like lead. The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive limits these components in electrical products. Keeping updated with such regulations contributes to healthier work environments.
**Tip:** Use cables certified eco-friendly. They reduce potential health risks.
In summary, awareness of safety regulations is a continuous process. Projects must adapt as standards evolve. Regular training and updates can bridge this knowledge gap.
| Cable Type | Description | Typical Applications | Safety Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Twisted Pair | Consists of pairs of wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference. | Telecommunications, networking. | ANSI/TIA-568 |
| Coaxial Cable | Features a central conductor surrounded by insulation, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer. | Cable television, internet connections. | IEEE 802.3 |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Uses light to transmit data through glass or plastic fibers, offering high-speed communication. | High-speed internet, telecommunications. | TIA-568, NEC |
| Power Cable | Used for the transmission of electricity; available in many sizes and types. | Residential and commercial power supply. | IEEE C2, NEC |
| Single-Core Cable | A single wire conductor insulated to carry electrical currents. | Lighting, control circuits. | IEC 60228 |
| Multi-Core Cable | Composed of multiple wires within a single sheath for various electrical applications. | Instrumentation, data transfer. | IEC 60228 |
| Shielded Cable | Includes a conductive layer to protect against electromagnetic interference. | Audio, video, and high-frequency applications. | ANSI/TIA-568 |
| USB Cable | Standard cable used for data transfer and power supply between devices. | Peripheral connections, charging. | USB-IF Standards |
| HVAC Cable | Specifically designed for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. | Control circuits for HVAC systems. | NEC, UL Standards |
| Ruggedized Cable | Designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures and moisture. | Industrial applications, outdoor use. | MIL-STD-810 |





At Radix, we do more than sell products; we provide solutions. We take the time to learn about each customer and your unique challenges, and then our knowledgeable team of problem solvers works to educate you on the possibilities to improve your products or operations.
From cutting-edge technology applications to extreme industrial environments, we’re here to collaborate, innovate, and elevate your success. Let’s connect.
